Service models
Sjogren’s Syndrome
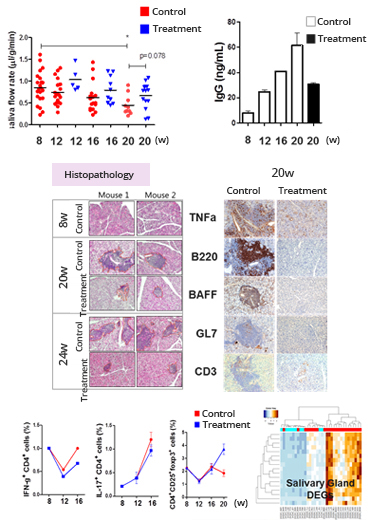
We provide efficacy evaluation services for candidate drugs targeting Sjogren’s syndrome using an animal model whereby an induced Type I diabetes changes epithelial tissues of salivary gland in 12 weeks, worsens lymphocytic inflammation in 16 weeks and reduces saliva excretion.
| Model | Evaluation interval | Evaluation items |
|---|---|---|
| NOD/ShiltJ female mice |
10, 12, 14, 16, 18 weeks 10, 12, 14, 16, 18 weeks 18 weeks 18 weeks |
|
Service analysis
Animal model
- Salivary flow rate
- Weight changes
- Blood glucose level
- Serum IgG
Salivary gland
- Analysis of lymphocyte foci area
- Detection of T cell infiltration (CD3 positive cell)
- Detection of B cell infiltration (B220 positive cell)
- Detection of inflammatory cytokine (TNF-a, BAFF)
- Detection of germinal center formation (GL-7)
- Flow cytometry of immune T cells (Th1, Th17, Treg)*
- Comparison of gene expression microarray*
Lachrymal gland (over 20 weeks)*
- Analysis of lymphocyte foci area
- Detection of T cell infiltration (CD3 positive cell)
- Detection of B cell infiltration (B220 positive cell)
- Detection of inflammatory cytokine (TNF-a, BAFF)
Cells derived from Sjogren’s syndrome patients
- Open to negotiation with researcher